Homework Assignments: Lesson 5 & 6
Contents:
- 5.1: Drawables, Themes, Styles
- 5.2: Material Design
- 5.3: Providing Resources for Adaptive Layouts
- 6.1: Testing the User Interface
5.1: Drawables, Themes, Styles
Build and run an app
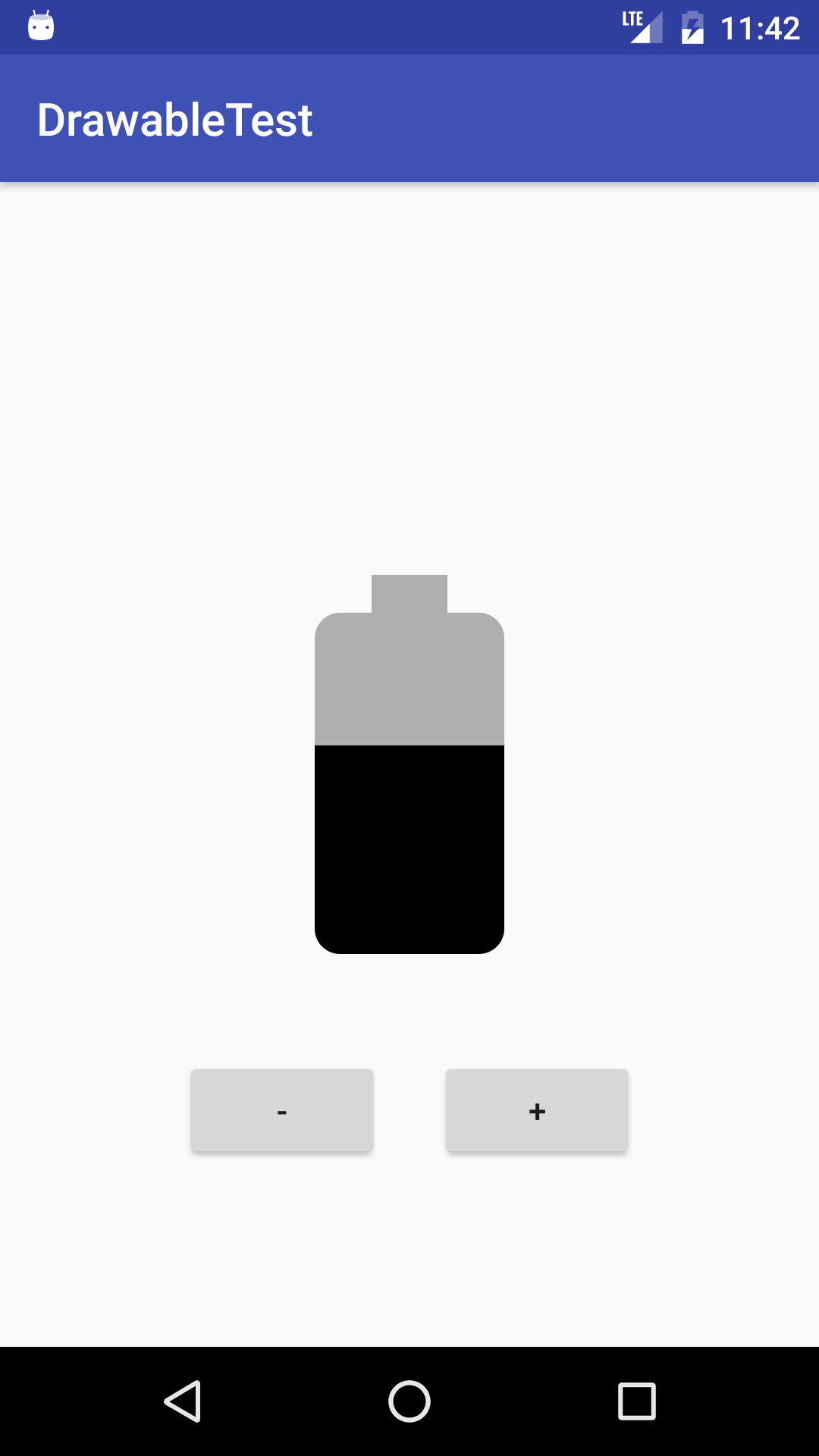
Create an app that displays an ImageView and plus and minus buttons, as shown below. The ImageView contains a level list drawable that is a battery level indicator. Pressing the plus or minus button changes the level of the indicator. Use the battery icons from the Vector Asset Studio to represent 7 different values for the battery level.
The app has the following properties:
- The plus button increments the level, causing the battery indicator to appear more full.
- The minus button decrements the level, causing the indicator to empty one level.

Answer these questions
Question 1
What two types of drawables do you use to create a button that displays text, where the button has one background when it is active and a different background when it is disabled, and both backgrounds are stretched when the size of the button is larger than the text it contains?
LevelListDrawableTransitionDrawableStateListDrawableNinePatchDrawable
Question 2
Suppose you create an app that has a dark background and light text, and the app doesn't need an ActionBar. Which base style does your application style inherit from?
Theme.AppCompat.LightTheme.AppCompat.Dark.NoActionBarTheme.AppCompat.NoActionBarTheme.NoActionBar
Submit your app for grading
Guidance for graders
- The buttons increment a count variable which is used to set the level on the ImageView using the
setImageLevel()method. - The levels in the LevelList drawable go from 0 to 6.
- The buttons'
onClickmethods check to see if the count variable is within the range of the level list drawable (0 - 6) before incrementing or decrementing the image level, so that you can't set a level that doesn't exist.
5.2: Material Design
Build and run an app
Open the MaterialMe app that you created in the LessonSupporting Landscape, Multiple Screen Sizes and Localization lesson.
- Create a shared element transition between the MainActivity and the DetailActivity, with the banner image for the sport as the shared element.
- Clicking on a list item in the MaterialMe app triggers the transition. The banner image from the card moves to the top of the screen in the Detail view.
Answer these questions
Question 1
Which color attribute in your style defines the color of the status bar?
colorPrimarycolorPrimaryDarkcolorAccentcolorAccentDark
Question 2
Which support library does the Floating Action Button belong to?
v4 Support Libraryv7 Support LibraryDesign Support LibraryCustom Button Support Library
Submit your app for grading
Guidance for graders
Check that the app has the following features:
- Window-content transitions are enabled in the app theme.
- A shared element transition is specified in the app style.
- The transition is defined as an XML resource.
- A common name is assigned to the shared elements in both layouts with the
android:transitionNameattribute. - The code uses the ActivityOptions.makeSceneTransitionAnimation() method.
5.3: Providing Resources for Adaptive Layouts
Build and run an app
Open the RecyclerView app that you created in the Create a Recycler View lesson. Modify the app to use a GridLayoutManager with the following column counts:
For a phone:
1 column in portrait
2 columns in landscape
For a tablet:
2 columns in portrait
3 columns in landscape

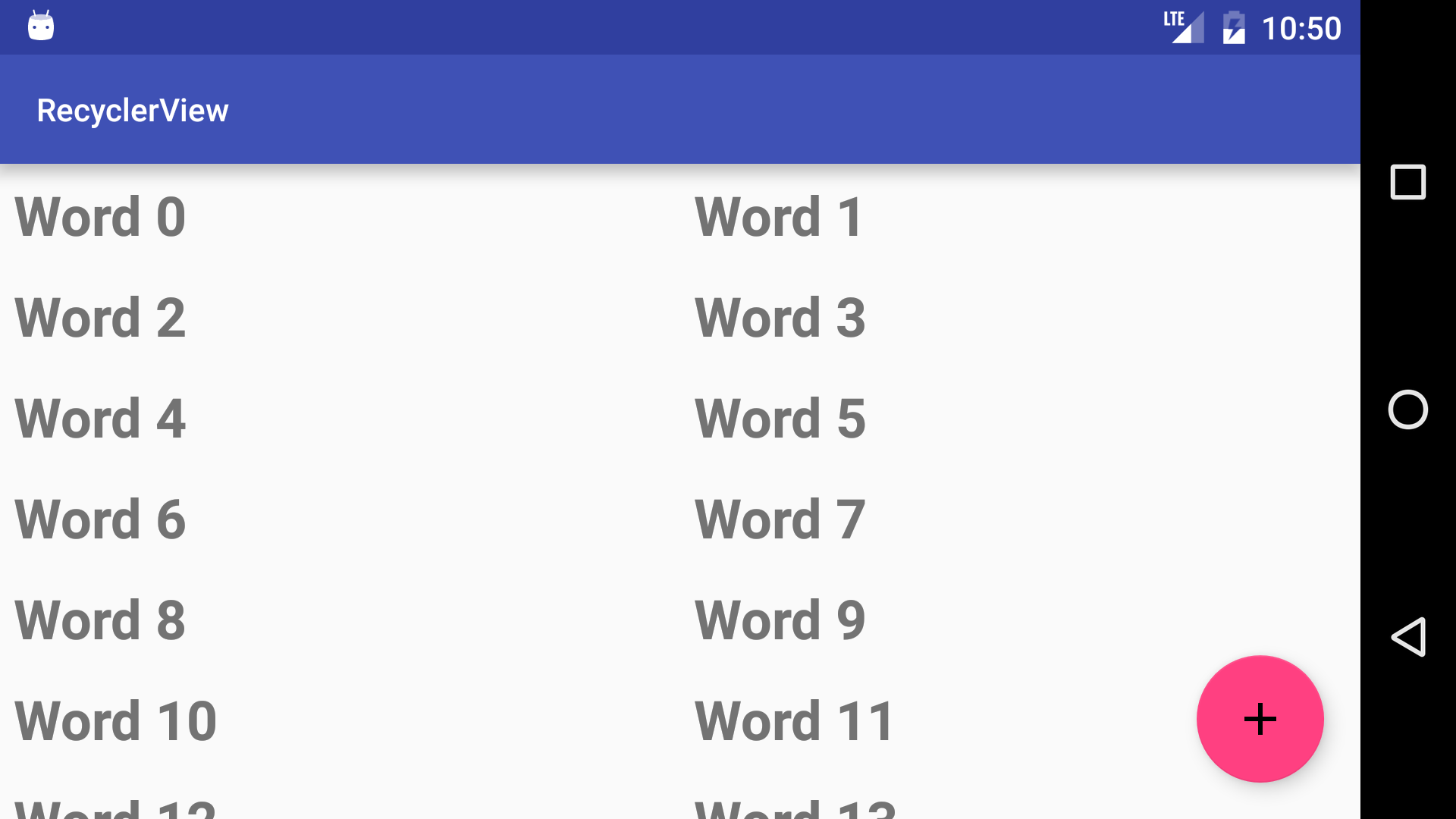
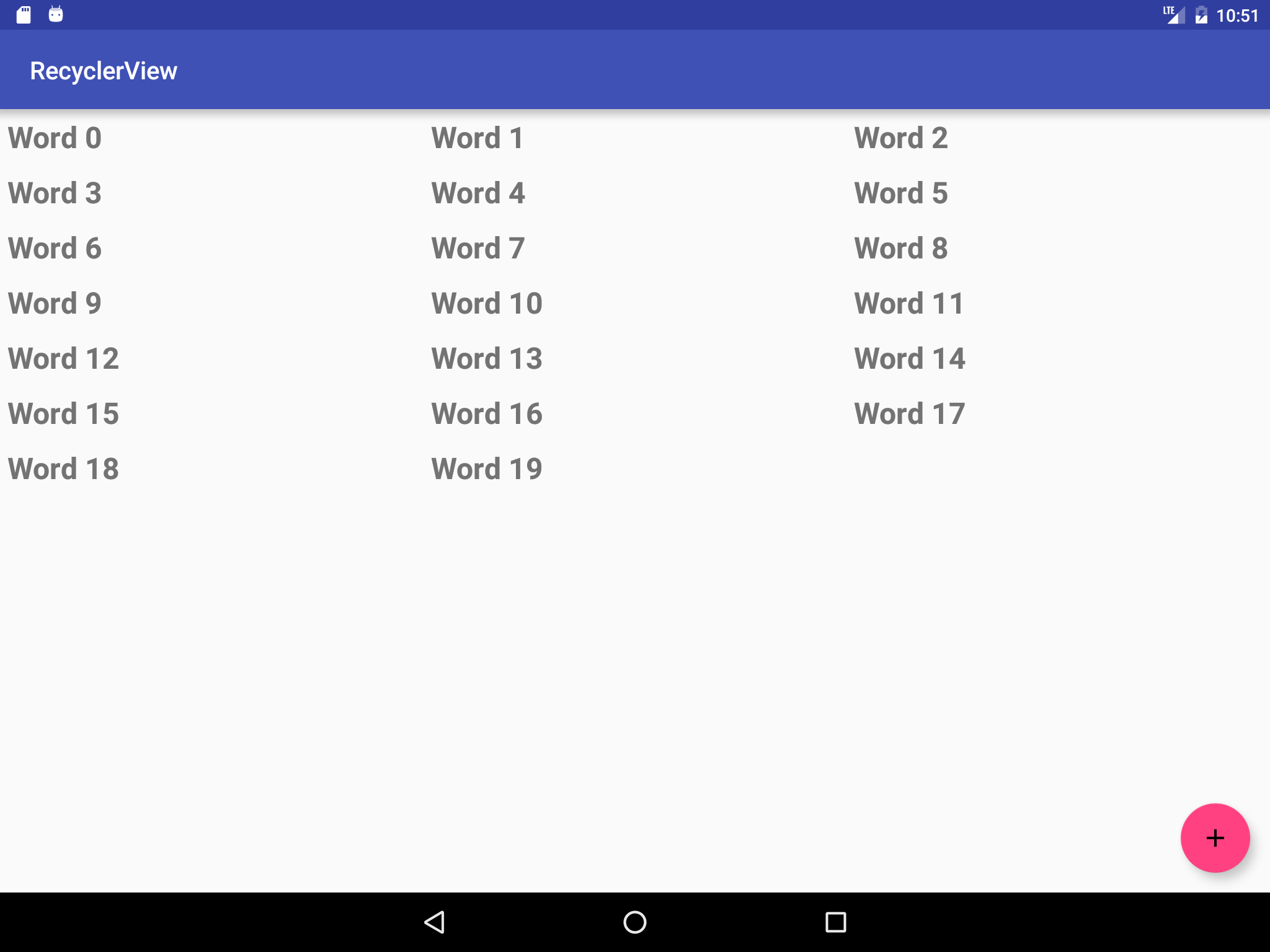
Answer these questions
Question 1
What resource qualifier is used to specify resources to be used when your app is in night mode?
Submit your app for grading
Guidance for graders
Check that the app has the following features:
- For phones and tablets in both landscape and portrait modes, the code includes resource-qualified values files that contain the integer for the column count.
- The app uses uses
getResources().getInteger()to retrieve a value from a resource file, then uses the value as the column count for grid layout.
6.1: Testing the User Interface
Write an Espresso test for the DroidCafe app (created in Chapter 4.3P) that tests the images in the main activity to make sure that they take the user to the second activity.
Build and run an app
Open the DroidCafe app that you created in previous lessons.
- Create an Espresso test as a Java class in the com.example.android.droidcafe (androidTest) folder (shown in Project: Android view in the java folder).
Create a test for each image in the MainActivity that:
Clicks the image.
Checks to see if the Order Activity appears.
Answer these questions
Question 1
Which steps do you perform to test an interaction, and in what order? Enter a number for each step, from 1 to 3, to specify the order:
- Match a view: Find a view to run the test.
- Assert and verify the result: Check the view's state to see if it reflects the expected state or behavior defined by the assertion.
- Perform an action: Perform a click or other action that triggers an event with the view.
Question 2
Which of the following annotations enables an instrumented JUnit 4 test class? Choose one:
@RunWith@Rule@Test
Question 3
Which of the following annotations establishes the context for the testing code? Choose one:
@RunWith@Rule@Test
Question 4
In this assignment, you need to test each image view used for navigation on the DroidCafe app main screen by clicking it. Would you use onView() to find each image view, or onData(), and why? Choose one:
- I would use
onData()because the view I want to find is an image view. - I would use
onView()because the view I want to find is in the current view hierarchy and appears on the screen. TheonData()method is for finding a child view in an AdapterView by first loading the view's adapter and then enabling the child view to appear on the screen. - I would use neither because the view is already in the current view hierarchy.
Submit your app for grading
Guidance for graders
Check that the app has the following features:
- Includes a test class in the com.example.android.droidcafe (androidTest) folder with the
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class)annotation. - Includes a separate test (annotated with
@Test) for each image. - Uses the
onView(),check(), andperform()methods. - Passes all tests.
