4.5: RecyclerView
Contents:
About RecyclerView
When you display a large number of items in a scrollable list, most of the items aren't visible. For example, in a long list of words or news headlines, the user only sees a few items at a time.
Or you may have a dataset that changes as the user interacts with it. If you create a new View every time the data changes, that's a lot of View items, even for a small dataset.
From a performance perspective, you want to conserve memory and save time:
- To conserve memory, minimize the number of
Viewitems that exist at any given point. - To save time, minimize the number of
Viewitems you have to create.
To accomplish both these goals, create more View items than the user can see on the screen and cache the created View items. Then reuse the View items with different data as list items scroll in and out of the display.
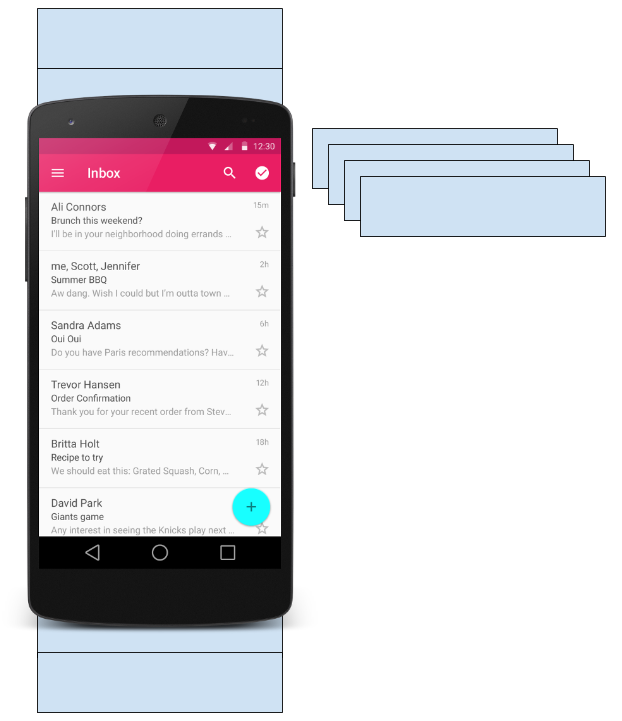
The RecyclerView class is a more advanced and flexible version of ListView. It's a container for displaying large, scrollable data sets efficiently by maintaining a limited number of View items.
Use RecyclerView when you need to display a large amount of scrollable data, or data collections whose elements change at runtime based on user action or network events.
RecyclerView components
To display data in a RecyclerView, you need the following (refer to the figure below):
- Data. It doesn't matter where the data comes from. You can create the data locally, as you do in the practical, get it from a database on the device as you will do in a later practical, or pull it from the cloud.
- A RecyclerView. The scrolling list that contains the list items.
An instance of
RecyclerViewas defined in theActivitylayout file to act as the container for theViewitems. - Layout for one item of data. All list items look the same, so you can use the same layout for all of them. The item layout has to be created separately from the
Activitylayout, so that oneViewitem at a time can be created and filled with data. - A layout manager. The layout manager handles the organization (layout) of user interface components in a
View. EachViewGrouphas a layout manager. ForLinearLayout, the Android system handles the layout for you.RecyclerViewrequires an explicit layout manager to manage the arrangement of list items contained within it. This layout could be vertical, horizontal, or a grid. The layout manager is an instance ofRecyclerview.LayoutManagerto organize the layout of the items in theRecyclerView. - An adapter. Use an extension of
RecyclerView.Adapterto connect your data to theRecyclerView. It prepares the data and how will be displayed in aViewHolder. When the data changes, the adapter updates the contents of the respective list item view in theRecyclerView. - A ViewHolder. Use an extension of
RecyclerView.ViewHolderto contain the information for displaying oneViewitem using the item's layout.
The diagram below shows the relationship between these components.
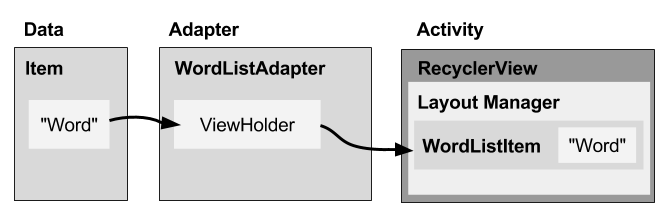
Data
Any displayable data can be shown in a RecyclerView.
- Text
- Images
- Icons
Data can come from any source.
- Created by the app. For example, scrambled words for a game.
- From a local database. For example, a list of contacts.
- From cloud storage or the internet. For example news headlines.
RecyclerView
A RecyclerView is a ViewGroup for a scrollable container. It is Ideal for long lists of similar items.
A RecyclerView uses a limited number of View items that are reused when they go off-screen. This saves memory and makes it faster to update list items as the user scrolls through data, because it is not necessary to create a new View for every item that appears.
In general, the RecyclerView keeps as many View items as can fit on the screen, plus a few extra at each end of the list to make sure that scrolling is fast and smooth.
Item Layout
The layout for a list item is kept in a separate XML layout file so that the adapter can create View items and edit their contents independently from the layout of the Activity.
Layout Manager
A layout manager positions View items inside a ViewGroup, such as the RecyclerView, and determines when to reuse View items that are no longer visible to the user. To reuse (or recycle) a View, a layout manager may ask the adapter to replace the contents of the View with a different element from the dataset. Recycling View items in this manner improves performance by avoiding the creation of unnecessary View items or performing expensive findViewById() lookups.
RecyclerView provides these built-in layout managers:
LinearLayoutManagershows items in a vertical or horizontal scrolling list.GridLayoutManagershows items in a grid.StaggeredGridLayoutManagershows items in a staggered grid.
To create a custom layout manager, extend the RecyclerView.LayoutManager class.
Animations
Animations for adding and removing items are enabled by default in RecyclerView. To customize these animations, extend the RecyclerView.ItemAnimator class and use the RecyclerView.setItemAnimator() method.
Adapter
An adapter helps two incompatible interfaces to work together. In a RecyclerView, the adapter connects data with View items. It acts as an intermediary between the data and the View. The adapter receives or retrieves the data, does any work required to make it displayable in a View, and places the data in a View.
For example, the adapter may receive data from a database as a Cursor object, extract the the word and its definition, convert them to strings, and place the strings in a View item that has two TextView elements—one for the word and one for the definition. You will learn more about cursors in a later chapter.
The RecyclerView.Adapter implements a ViewHolder, and must override the following callbacks:
onCreateViewHolder()inflates aViewitem and returns a newViewHolderthat contains it. This method is called when theRecyclerViewneeds a newViewHolderto represent an item.onBindViewHolder()sets the contents of aViewitem at a given position in theRecyclerView. This is called by theRecyclerView, for example, when a newViewitem scrolls onto the screen.getItemCount()returns the total number of items in the data set held by the adapter.
ViewHolder
A RecyclerView.ViewHolder describes a View item and metadata about its place within the RecyclerView. Each ViewHolder holds one set of data. The adapter adds data to each ViewHolder for the layout manager to display.
You define your ViewHolder layout in an XML resource file. It can contain (almost) any type of View, including clickable elements.
Implementing a RecyclerView
Implementing a RecyclerView requires the following steps:
- Add the
RecyclerViewdependency if needed (depending on which template is used for theActivity). - Add the
RecyclerViewto theActivitylayout. - Create a layout XML file for one
Viewitem. - Extend
RecyclerView.Adapterand implement theonCreateViewHolder()andonBindViewHolder()methods. - Extend
RecyclerView.ViewHolderto create aViewHolderfor your item layout. You can add click behavior by overriding theonClick()method. - In the
Activity, inside theonCreate()method, create aRecyclerViewand initialize it with the adapter and a layout manager.
Adding the dependency
The RecyclerView library (android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView) is part of the Support Library. Some Activity templates, such as the Basic Activity template, already include the Support Library dependency in the app's build.gradle (Module: app) file.
If Android Studio doesn't suggest <android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView when entering <RecyclerView in the layout editor, you need to add the Support Library dependency for RecyclerView to the dependencies section of the app's build.gradle (Module: app) file:
compile 'com.android.support:recyclerview-v7:26.1.0'
If Android Studio highlights the above dependency and suggests a newer version, enter the version numbers for the newer version.
Adding a RecyclerView to the Activity layout
Add the RecyclerView to the Activity layout file:
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recyclerview"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView>
Use the RecyclerView from the Support Library (android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView) to be compatible with older versions of Android. The only required attributes are the id, the layout_width, and the layout_height. For customizing with more attributes, add the attributes to the items, not to this RecyclerView, which is a ViewGroup.
Creating the layout for one item
Create an XML resource file and specify the layout of one item. The adapter uses this code to create the ViewHolder.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="6dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/word"
style="@style/word_title" />
</LinearLayout>
The TextView has a @style element. A style is a collection of properties that specifies the look of a View. You can use styles to share display attributes with multiple View elements. An easy way to create a style is to extract the style of a View element that you already created. For example, after styling a TextView:
- Right-click (or Control-click) the
TextView. - Choose Refactor > Extract > Style.
- Name your style, leave all other options selected, and select the Launch 'Use Style Where Possible' option. Then click OK.
- When prompted, apply the style to the Whole Project.
You learn more about styles in another lesson.
Creating an adapter with a ViewHolder
Extend RecyclerView.Adapter and implement the onCreateViewHolder() and onBindViewHolder() methods.
Create a new Java class with the following signature:
public class WordListAdapter extends
RecyclerView.Adapter<WordListAdapter.WordViewHolder> {
In the constructor, get an inflater from the current context, and your data.
public WordListAdapter(Context context, LinkedList<String> wordList) {
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
this.mWordList = wordList;
}
For this adapter, you have to implement three methods:
onCreateViewHolder()creates aViewand returns it.@Override public WordViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType){ // Inflate an item view. View mItemView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.wordlist_item, parent, false); return new WordViewHolder(mItemView, this); }onBindViewHolder()associates the data with theViewHolderfor a given position in theRecyclerView.@Override public void onBindViewHolder( WordViewHolder holder, int position) { // Retrieve the data for that position String mCurrent = mWordList.get(position); // Add the data to the view holder.wordItemView.setText(mCurrent); }getItemCount()returns to number of data items available for displaying.@Override public int getItemCount() { return mWordList.size(); }
Implementing the ViewHolder class
The ViewHolder class for your item layout is usually defined as an inner class to the adapter. Extend RecyclerView.ViewHolder to create the ViewHolder. You can add click behavior by overriding the onClick()method.
class WordViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
If you want to add click handling, you need to implement View.onClickListener. One way to do this is to have the ViewHolder implement the View.onClickListener methods.
// Extend the signature of WordViewHolder to implement a click listener.
class WordViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder
implements View.OnClickListener {
In its constructor, the ViewHolder has to inflate its layout, associate with its adapter, and, if applicable, set a click listener.
public WordViewHolder(View itemView, WordListAdapter adapter) {
super(itemView);
wordItemView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.word);
this.mAdapter = adapter;
itemView.setOnClickListener(this);
}
And, if you implementing View.onClickListener, you also have to implement onClick().
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
wordItemView.setText ("Clicked! "+ wordItemView.getText());
}
If you want to attach click listeners to other elements of the ViewHolder, do that dynamically in onBindViewHolder() (you will do this in another practical).
Creating the RecyclerView
Finally, to tie it all together, add to the Activity the following:
- Declare a
RecyclerView.private RecyclerView mRecyclerView; - In the
ActivityonCreate()method, get a handle to theRecyclerViewin the layout:mRecyclerView = findViewById(R.id.recyclerview); - Create an adapter and supply the data to be displayed.
mAdapter = new WordListAdapter(this, mWordList); - Connect the adapter with the
RecyclerView.mRecyclerView.setAdapter(mAdapter); - Give the
RecyclerViewa default layout manager.mRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this));RecyclerViewis an efficient way to display scrolling list data. It uses the adapter pattern to connect data with list item views. To implement aRecyclerView, you need to create an adapter and aViewHolder. You also need to create the methods that take the data and add it to the list items.
Related practical
The related practical is 4.5: RecyclerView.
Learn more
Android Studio documentation:
Android developer documentation:
RecyclerViewLayoutInflatorRecyclerView.LayoutManagerLinearLayoutManagerGridLayoutManagerStaggeredGridLayoutManagerCoordinatorLayoutConstraintLayoutRecyclerView.AdapterRecyclerView.ViewHolderView.onClickListener- Create a list with
RecyclerView
Video: