11.2: Creating a SurfaceView object
Contents:
- What you should already KNOW
- What you will LEARN
- What you will DO
- App overview
- Task 1. Create the SurfaceView example app
- Solution code
- Summary
- Related concept
- Learn more
When you create a custom view and override its onDraw() method, all drawing happens on the UI thread. Drawing on the UI thread puts an upper limit on how long or complex your drawing operations can be, because your app has to complete all its work for every screen refresh.
One option is to move some of the drawing work to a different thread using a SurfaceView.
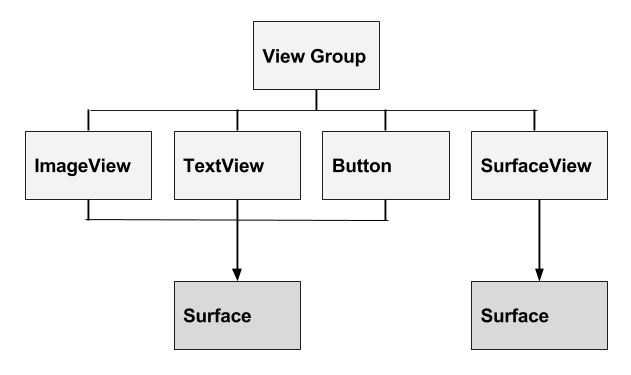
- All the views in your view hierarchy are rendered onto one
Surfacein the UI thread. - In the context of the Android framework,
Surfacerefers to a lower-level drawing surface whose contents are eventually displayed on the user's screen. - A
SurfaceViewis a view in your view hierarchy that has its own separateSurface, as shown in the diagram below. You can draw to it in a separate thread. - To draw, start a thread, lock the
SurfaceView's canvas, do your drawing, and post it to theSurface.
The following diagram shows a View Hierarchy with a Surface for the views and another separate Surface for the SurfaceView.
What you should already KNOW
You should be able to:
- Create a custom
View. - Draw on and clip a
Canvas. - Add event handlers to views.
- Understand basic threading.
What you will LEARN
You will learn how to:
- How to use a
SurfaceViewto draw to the screen from a different thread. - A basic app architecture for simple games.
What you will DO
- Create an app that uses a
SurfaceViewto implement a simple game.
App overview
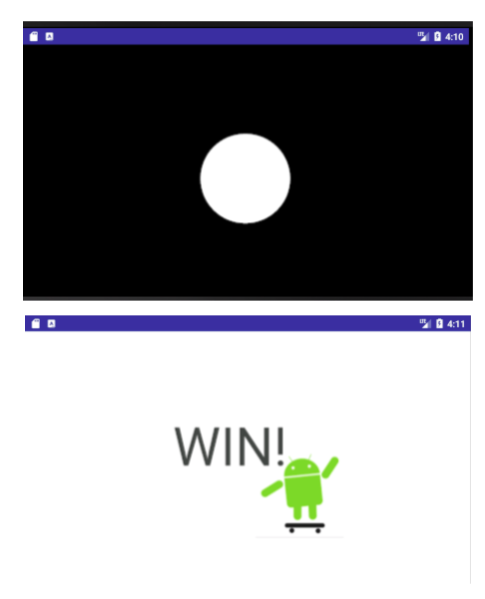
The SurfaceViewExample app lets you search for an Android image on a dark phone screen using a "flashlight."
- At app startup, the user sees a black screen with a white circle, the "flashlight."
- While the user drags their finger, the white circle follows the touch.
- When the white circle intersects with the hidden Android image, the screen lights up to reveal the complete image and a "win" message.
- When the user lifts their finger and touches the screen again, the screen turns black and the Android image is hidden in a new random location.
The following is a screenshot of the SurfaceViewExample app at startup, and after the user has found the Android image by moving around the flashlight.
Additional features:
- Size of the flashlight is a ratio of the smallest screen dimension of the device.
- Flashlight is not centered under the finger, so that the user can see what's inside the circle.
Task 1. Create the SurfaceViewExample app
You are going to build the SurfaceViewExample app from scratch. The app consists of the following three classes:
- MainActivity—Locks screen orientation, gets the display size, creates the
GameView, and sets theGameViewas its content view. OverridesonPause()andonResume()to pause and resume the game thread along with theMainActivity. - FlashlightCone—Represents the cone of a flashlight with a radius that's proportional to the smaller screen dimension of the device. Has get methods for the location and size of the cone and a set method for the cone's location.
- GameView—A custom
SurfaceViewwhere game play takes place. Responds to motion events on the screen. Draws the game screen in a separate thread, with the flashlight cone at the current position of the user's finger. Shows the "win" message when winning conditions are met.
1.1 Create an app with an empty activity
- Create an app using the Empty Activity template. Call the app SurfaceViewExample.
- Uncheck Generate Layout File. You do not need a layout file.
1.2 Create the FlashlightCone class
- Create a Java class called
FlashlightCone.public class FlashlightCone {} - Add member variables for x, y, and the radius.
private int mX; private int mY; private int mRadius; Add methods to get values for x, y, and the radius. You do not need any methods to set them.
public int getX() { return mX; } public int getY() { return mY; } public int getRadius() { return mRadius; }- Add a constructor with integer parameters
viewWidthandviewHeight. - In the constructor, set
mXandmYto position the circle at the center of the screen. - Calculate the radius for the flashlight circle to be one third of the smaller screen dimension.
public FlashlightCone(int viewWidth, int viewHeight) { mX = viewWidth / 2; mY = viewHeight / 2; // Adjust the radius for the narrowest view dimension. mRadius = ((viewWidth <= viewHeight) ? mX / 3 : mY / 3); } - Add a
publicvoid update()method. The method takes integer parametersnewXandnewY, and it setsmXtonewXandmYtonewY.public void update(int newX, int newY) { mX = newX; mY = newY; }
1.3 Create a new SurfaceView class
- Create a new Java class and call it
GameView. - Let it extend
SurfaceViewand implementRunnable.Runnableadds arun()method to your class to run its operations on a separate thread.public class GameView extends SurfaceView implements Runnable {} - Implement methods to add a stub for the only required method,
run().@Override public void run(){} Add the stubs for the constructors and have each constructor call
init().public GameView(Context context) { super(context); init(context); } public GameView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); init(context); } public GameView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); init(context); }- Add private
init()method and set themContextmember variable tocontext.private void init(Context context) { mContext = context; } - In the
GameViewclass, add stubs for thepause()andresume() methods. Later, you will manage your thread from these two methods.
1.4 Finish the MainActivity
In
MainActivity, create a member variable for theGameViewclass.private GameView mGameView;In the
onCreate()method:Lock the screen orientation into landscape. Games often lock the screen orientation.
setRequestedOrientation(ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE);- Create an instance of
GameView. - Set
mGameViewto completely fill the screen. - Set
mGameViewas the content view forMainActivity.mGameView = new GameView(this); // Android 4.1 and higher simple way to request fullscreen. mGameView.setSystemUiVisibility(View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_FULLSCREEN); setContentView(mGameView); - Still in
MainActivity, override theonPause()method to also pause themGameViewobject. ThisonPause()method shows an error, because you have not implemented thepause()method in theGameViewclass.@Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); mGameView.pause(); } - Override
onResume()to resume themGameView. TheonResume()method shows an error, because you have not implemented theresume()method in theGameView.@Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); mGameView.resume(); }
1.5 Finish the init() method for the GameView class
In the constructor for the GameView class:
- Assign the
contexttomContext. - Get a persistent reference to the
SurfaceHolder. Surfaces are created and destroyed by the system while the holder persists. - Create a
Paintobject and initialize it. Create a
Pathto hold drawing instructions. If prompted, importandroid.graphics.Path.
Here is the code for the
init()method.private void init(Context context) { mContext = context; mSurfaceHolder = getHolder(); mPaint = new Paint(); mPaint.setColor(Color.DKGRAY); mPath = new Path(); }- After copy/pasting the code, define the missing member variables.
1.6 Add the setUpBitmap() method to the GameView class
The setUpBitmap() method calculates a random location on the screen for the Android image that the user has to find. You also need a way to calculate whether the user has found the bitmap.
- Set
mBitmapXandmBitmapYto random x and y positions that fall inside the screen. - Define a rectangular bounding box that contains the Android image.
- Define the missing member variables.
private void setUpBitmap() { mBitmapX = (int) Math.floor( Math.random() * (mViewWidth - mBitmap.getWidth())); mBitmapY = (int) Math.floor( Math.random() * (mViewHeight - mBitmap.getHeight())); mWinnerRect = new RectF(mBitmapX, mBitmapY, mBitmapX + mBitmap.getWidth(), mBitmapY + mBitmap.getHeight()); }
1.7 Implement the methods to pause and resume the GameView class
The pause() and resume() methods on the GameView are called from the MainActivity when it is paused or resumed. When the MainActivity pauses, you need to stop the GameView thread. When the MainActivity resumes, you need to create a new GameView thread.
Add the
pause()and resume()methods using the code below. ThemRunningmember variable tracks the thread status, so that you do not try to draw when the activity is not running anymore.public void pause() { mRunning = false; try { // Stop the thread (rejoin the main thread) mGameThread.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } public void resume() { mRunning = true; mGameThread = new Thread(this); mGameThread.start(); }- As before, add the missing member variables.
Thread management can become a lot more complex after you have multiple threads in your game. See Sending Operations to Multiple Threads for lessons in thread management.
1.8 Implement the onSizeChanged() method
There are several ways in which to set up the view after the system has fully initialized the view. The onSizeChangedMethod() is called every time the view changes.The view starts out with 0 dimensions. When the view is first inflated, its size changes and onSizeChangedMethod() is called. Unlike in onCreate(), the view's correct dimensions are available.
- Get the image of Android on a skateboard from github and add it to your drawable folder, or use a small image of your own choice.
In
GameView, override theonSizeChanged()method. Both the new and the old view dimensions are passed as parameters as shown below.@Override protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) { super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh); }Inside the
onSizeChanged()method:Store the width and height in member variables
mViewWidthandmViewHeight.mViewWidth = w; mViewHeight = h;- Create a
FlashlightConeand pass inmViewWidthandmViewHeight.mFlashlightCone = new FlashlightCone(mViewWidth, mViewHeight); - Set the font size proportional to the view height.
mPaint.setTextSize(mViewHeight / 5); - Create a
Bitmapand callsetupBitmap().mBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource( mContext.getResources(), R.drawable.android); setUpBitmap();
1.9 Implement the run() method in the GameView class
The interesting stuff, such as drawing and screen refresh synchronization, happens in the run() method. Inside your run() method stub, do the following:
- Declare a
Canvascanvasvariable at the top of therun()method:Canvas canvas; Create a loop that only runs while
mRunningis true. All the following code must be inside that loop.while (mRunning) { }Check whether there is a valid
Surfaceavailable for drawing. If not, do nothing.if (mSurfaceHolder.getSurface().isValid()) {All code that follows must be inside this
ifstatement.Because you will use the flashlight cone coordinates and radius multiple times, create local helper variables inside the
ifstatement.int x = mFlashlightCone.getX(); int y = mFlashlightCone.getY(); int radius = mFlashlightCone.getRadius();Lock the canvas.
In an app, with more threads, you must enclose this with atry/catchblock to make sure only one thread is trying to write to theSurface.
canvas = mSurfaceHolder.lockCanvas();
- Save the current canvas state.
canvas.save(); - Fill the canvas with white color.
canvas.drawColor(Color.WHITE); - Draw the Skateboarding Android bitmap on the canvas.
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap, mBitmapX, mBitmapY, mPaint); - Add a circle that is the size of the flashlight cone to
mPath.mPath.addCircle(x, y, radius, Path.Direction.CCW); - Set the circle as the clipping path using the
DIFFERENCEoperator, so that's what's inside the circle is clipped (not drawn).canvas.clipPath(mPath, Region.Op.DIFFERENCE); - Fill everything outside of the circle with black.
canvas.drawColor(Color.BLACK); - Check whether the the center of the flashlight circle is inside the winning rectangle. If so, color the canvas white, redraw the Android image, and draw the winning message.
if (x > mWinnerRect.left && x < mWinnerRect.right && y > mWinnerRect.top && y < mWinnerRect.bottom) { canvas.drawColor(Color.WHITE); canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap, mBitmapX, mBitmapY, mPaint); canvas.drawText( "WIN!", mViewWidth / 3, mViewHeight / 2, mPaint); } - Drawing is finished, so you need to rewind the path, restore the canvas, and release the lock on the canvas.
Run your app. It should display a black screen with a white circle at the center of the screen.mPath.rewind(); canvas.restore(); mSurfaceHolder.unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas);
1.10 Respond to motion events
For the game to work, your app needs to detect and respond to the user's motions on the screen.
In
GameView, override theonTouchEvent()method and update the flashlight position on theACTION_DOWNandACTION_MOVEevents.@Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { float x = event.getX(); float y = event.getY(); // Invalidate() is inside the case statements because there are // many other motion events, and we don't want to invalidate // the view for those. switch (event.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: setUpBitmap(); updateFrame((int) x, (int) y); invalidate(); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: updateFrame((int) x, (int) y); invalidate(); break; default: // Do nothing. } return true; }- Implement the
updateFrame()method called inonTouchEvent()to set the new coordinates of theFlashlightCone.private void updateFrame(int newX, int newY) { mFlashlightCone.update(newX, newY); } - Run your app and GAME ON!
- After you win, tap the screen to play again.
Solution code
Android Studio project: SurfaceViewExample
Summary
- To offload drawing to a different thread, create a custom view that extends
SurfaceViewand implementsRunnable. TheSurfaceViewis part of your view hierarchy but has a drawingSurfacethat is separate from the rest of the view hierarchy. - Create an instance of your custom view and set it as the content view of your activity.
- Add
pause()andresume()methods to theSurfaceViewthat stop and start a thread. - Override
onPause()andonResume()in the activity to call thepause()andresume()methods of theSurfaceView. - If appropriate, handle touch events, for example, by overriding
onTouchEvent(). - Add code to update your data.
In the
SurfaceView, implement therun()method to:- Check whether a
Surfaceis available. - Lock the canvas.
- Draw.
- Unlock the canvas and post to the
Surface.
- Check whether a
Related concept
The related concept documentation is in The SurfaceView class.
Learn more
Android developer documentation:
SurfaceViewclassSurfaceHolderinterfaceRunnableinterface- Sending Operations to Multiple Threads
PaintclassPathclassClippingBasiccode sample- Graphics architecture for a comprehensive introduction
